How can “the intersection of creative marketing, automation, and smart use of data” help you grow? Read on…
This article originally appeared as a guest post for the Midem blog.
Instead of hiring marketing managers, startups are recruiting growth hackers to work on more sustainable deliverables than just ‘dumb traffic’. How can growth hacking be used by artists and labels? Let’s start with the most common growth hack in the music business.
Chart manipulation
Being at the top of iTunes or Beatport charts can make such a big difference in sales that the act of getting a big group of fans to buy a track or album simultaneously has been turned into an art. The phenomenon has also become subject to dodgy practices akin to buying followers for social media accounts with countless companies popping up offering to get you into digital music store charts for a fee. This is a poor strategy, because if caught, you’ll be removed from the charts completely and perhaps suffer further penalties for breaking the store’s terms of service.
A more sustainable strategy for influencing the charts, with no marketing budget, should include building engaged followings on various social media platforms, so that you can create hype prior to release, get the release date into everyone’s heads and give people a feeling that they’re part of something larger than themselves come the release date rush to play or purchase your music. That’s not really growth hacking though, because for any strategy to be scaleable, you need to be able to automate it.
What is growth hacking?
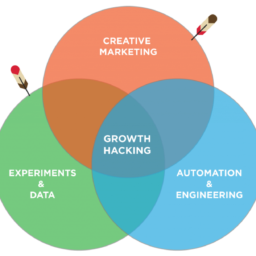
There are a lot of definitions for growth hacking, but the clearest is probably Growth Tribe’s (top image; click for full size), which explains growth hacking as the intersection of creative marketing, automation, and smart use of data.
Famous examples of growth hacking include Airbnb’s crawling and reposting of Craigslist listings, and Dropbox’s encouragement of word of mouth and referrals.
To hack growth successfully, you need to set clear goals. For this, you can use the AARRR framework, which divides growth into the following steps:
- Acquisition
- Activation
- Retention
- Referral
- Revenue
It’s a more practical model than the AIDA model most marketers are familiar with (Attention, Interest, Desire, Action), because it’s easier to define actionable goals by it.
Since the AARRR framework is usually applied to services, we have to redefine some of the words to make sense when applied to the music business. To make it easy, we’ll follow the ecosystem approach of developing your business as an artist, which means building up a fanbase (henceforth referred to as tribe), keeping it engaged and monetising it by carefully listening to it and understanding opportunities.
Acquisition & activation
The first step is to get your music discovered and then having a way to get back onto the radar of the people who discovered your music. Nowadays most music platforms have a Follow function, so it has gotten significantly easier than just a few years ago. Other than that, make sure your music ALWAYS has complete metadata. Having a very recognisable sound also helps. Now let’s growth hack.
Don’t believe the hype: email newsletters are still a valuable tool for communicating with your tribe. Posts made on social media platforms are fleeting and can be missed either through noise or because of algorithmic filtering. Just jump into your Twitter analytics panel and compare the number of impressions with your total number of followers. It’s likely around 10%. Even quite poor newsletters have higher open rates than that. Besides this, email newsletters give you great data, so that you know who opened your newsletter, what links they clicked, and more.
Setting up a newsletter
Since you need to automate your processes, you won’t be sending your newsletters from Gmail with your mailinglist in BCC. Use a good tool, like MailChimp or Revue. Decide about what kind of content you want to feature and how regularly you want to send something out. Consistency is key.
These tools will give you a bit of code that you can use to easily subscribe people to your mailinglist through Twitter Cards. Twitter Cards are a type of ad format which allow you to collect people’s email addresses with 1 click. You can keep campaigns paused, so you can use these Twitter Cards completely free of charge. Here’s an example (and shameless self-promotion).
They can be a bit tricky to set up, but persevere. It’s worth it!
Twitter Cards can be linked to, just like individual tweets can be linked to. This means that in your welcome email, you can ask people to retweet your Twitter Card so that their followers can also subscribe with 1 click. Now, every time someone subscribes, you have a good chance they’ll refer new subscribers. Automation in action.

You can pin your Twitter Card to the top of your profile so that everyone sees it. You can also use a tool like Zapier or IFTTT to automatically tweet to new followers to make them aware of your new release, newsletter or simply to strike up a conversation. Just don’t be too spammy about it.
Now you have set up a simple hack that:
- Helps you stay in touch with your tribe through email
- Converts Twitter followers to email subscribers
- Helps you get referrals
- Engages new Twitter followers
Retention
Online services usually measure retention by looking at repeat users or customers, such as weekly or monthly active users. Unless an artist app is central to your strategy, you will probably have to define retention in a different way.
Should you focus on your newsletter, then it’s important to understand how you can get more people to consistently open your newsletter and click where you want them to click. This is not about the total subscriber count, what matters is the percentage of subscribers that open, and the percentage of openers that click. Actions performed post-click may matter too (eg. sales).
Should you prefer to focus on music playback, you can use Spotify’s Fan Insights platform (for instance), to understand the sizes of segments of your listener base, such as:
- Streakers; people who’ve listened to your music every day in the last week
- Loyalists; people who’ve listened to you more than any other artist
- Regulars; people who’ve listened to you on the majority of the days in the last month
Knowing this data, you can then set up experiments, such as scheduling tweets throughout a month that promote a particular release, to see if you can influence these numbers positively and attain more regulars, loyalists or streakers. You can use this simple guide for effectively gathering and scheduling interesting things to post to your social media channels using Pocket and Buffer.
You will be able to see the click through rates through your Twitter or Buffer analytics, so you can experiment with different messages to see what works best. You can also sign up to Bitly to generate unique links that give additional data.
Referral
If you’ve ever tried to download a ‘free’ track on Soundcloud, you’ve probably come across tools that make you follow accounts and repost tracks before you get access to your download. It seems like a good growth hack. A download for some exposure sounds like a fair trade. However you need to consider the experience of this fan who likes your music so much that they actually want to save it offline.
These people have invested a lot of time in following artists and curators to get a great feed of music that they can check out when they want to hear something new. Users go on discovery sprees and afterwards go to their liked tracks to grab the free downloads. Having to go through 10 different platforms, following scores of random accounts and curators and spamming your friends with reposted playlists when you only liked one track in there… that’s a pretty crappy experience. There goes their carefully curated feed.
Here’s the awesome thing about referrals: when people really love something, they want to share it. When people share your music, they deepen their commitment. When you force people to share things they would have shared anyway, you take away all of the meaning in the act. You need to channel the love people have for your music, make people feel like they’re part of something bigger than themselves and drive them to perform an action with purpose.
Let’s say your goal is to create buzz around a certain release, so that you can get high on the charts on release date. Your incentive: an exclusive pre-release livestream where you present your new project. The method we’ll use is “Flock to Unlock”:
- You get people to retweet a certain tweet;
- You set up Zapier to automatically reply to retweeters and send them an invitation code (can be as simple as tweeting a link to a Typeform which collects email addresses);
- The reward only gets unlocked after you’ve reached a certain number of retweets.
The fact that the retweet count is public, makes people feel like they have a shared goal; that they are part of something bigger than themselves… a movement!
Yes, people who keep a close eye on your feed might be able to get into the stream without retweeting. You don’t lose anything. Don’t worry about that. You could add a bit of text to the Typeform and appeal to people that if they haven’t retweeted, it would mean a lot to you if they would do so anyway. Reciprocity is a powerful dynamic.
During the unlocked livestream, you can thank everybody and tell them it’s important to you that if people want to buy your release, they do so on the day it comes out. If they want to support in other ways, explain how they can share social media posts on the day itself. Again, make them feel like they’re part of something bigger than themselves. This helps you hack the charts and get new fans and more sales.
Another example are Yellow Claw’s mixtapes, which promote highly anticipated unreleased music. The mixtapes are so popular that the group even makes creative trailers to promote their mixtapes. Hype upon hype upon hype. It has worked well for them.
If you’re clever, you can create a simple tool that lets fans connect their Twitter accounts and then they’ll automatically retweet one of your tweets on the day of release. It’s quite likely that such tools actually exist, but make sure to do a little bit of research into the company before you ask your fans to connect their accounts to them.
Make sure to test your tweets! By spending $10-20 through Twitter Ads, you can easily test which messages get the most engagement, so that on the day itself, you’ll know exactly what the best things to tweet are.
Revenue
If your goal is to be able to make a living as an artist, then ultimately all of these steps should lead to increased revenue. If you can activate your following, it means more sales and more streams both directly and indirectly through network effects.
Having an engaged following gives opportunities for more exciting types of business models. You can create a fan club with all kinds of exclusives for anyone who’s a member. Look at Kickstarter, Patreon or PledgeMusic for great examples of the type of things you can offer to your most hardcore fans. Having a membership model opens up a lot of options and experiments you can do to better monetise your following, such as:
- Significant discounts on annual membership plans
- First month free trials
- 15% discount for life
- Temporary discounts with countdowns to give people a sense of urgency
It also changes what types of products you can offer, because you can go way beyond music streams and sales.
Fan clubs can be set up with tools like Drip, Fullscreen Direct, Music Glue and SupaPass. They offer different pricing models, so take some time to figure out which tool best suits your short and long-term needs. This list is not exhaustive, so also look at similar services and competitors.
How to decide what to do first
Any growth hacking starts with brainstorming. There are a million things you can be doing. What goes first? The answer is PIE.
- Probability: how likely is this to succeed?
- Impact: how big of an impact will it have on my core metric?
- Ease: how easy is it to setup or implement this?
Score them, rank them, and then you have your list of priorities.
Understand that you’re building funnels, so focusing on getting more revenue out of your total of 2 fans is probably not the right priority.
Double down on what works
If you’re trying out 10 things with mixed results, but you’ve verified that 1 or 2 channels are performing really well, then scrap the other 8 and focus on these 2. The goal is not to be doing as many things as possible. The goal is to measure what works best, so that you can focus on that and move on to the next experiment. Remember: Build, Measure, Learn.
It might all seem overwhelming, but over the next days, look at all the things you’re already doing. What social media channels are you using, how do you distribute your music, what kind of info do you collect from your fans, etc. Look at small things you can improve, such as better use of hashtags or more consistent posting schedules. Then try to automate something.
It’s a learning process and you need to make it fun for yourself. Let your curiosity drive you. None of the above examples might be relevant for you and your fans, so find out what works for you. Constantly look for ways where a small investment of time will save you loads of time in the future. There is always something to improve, something new to try out.
Enjoy the journey.
Extra resources:
Marketing Stack – a great directory for growth hacking tools.
The Definitive Guide to Growth Hacking – a very extensive, infographic style, guide to growth hacking with loads of examples and good depth.
Growth Tribe’s e-course – a free email course in growth hacking
GrowthHackers.com – a community portal for growth hackers with loads of fresh info, case studies, and discussions.